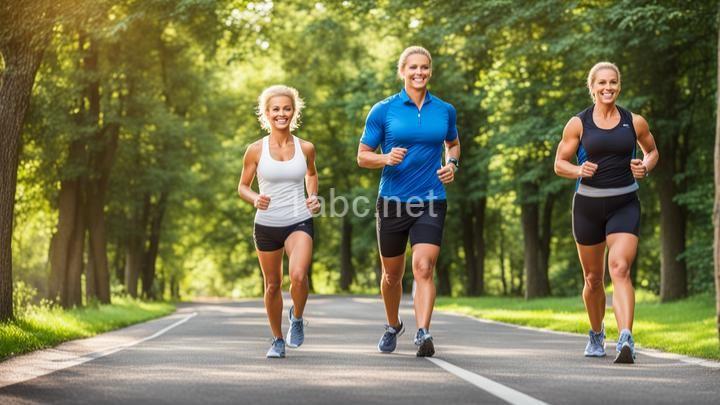
The Role of Exercise in Managing Diabetic Complications

Introduction:
Living with diabetes can be challenging, but there are various ways to effectively manage the condition and reduce the risk of complications. One such method is exercise. Not only does exercise help control blood sugar levels, but it also has numerous physical and emotional health benefits. In this article, we will explore the different types of diabetic complications, the benefits of exercise for diabetic individuals, the various types of exercises suitable for them, and tips for incorporating exercise into their daily routine.
Understanding Diabetic Complications:
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels. If left unmanaged, it can lead to various complications. Diabetic complications refer to the long-term effects of diabetes on different parts of the body, including the heart, eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Some common types of complications associated with diabetes include cardiovascular disease, retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy. These complications can significantly impact daily life, making it essential for individuals with diabetes to actively manage their condition.
Benefits of Exercise for Diabetic Individuals:
Physical Health Benefits:
Regular exercise plays a crucial role in managing diabetes and its associated complications. One of the significant benefits of exercise is its ability to control blood sugar levels. When you engage in physical activity, your muscles use glucose for energy, leading to a decrease in blood sugar levels. This can help individuals with diabetes maintain stable blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia.
Furthermore, exercise has a positive impact on heart health. It improves cardiovascular fitness, strengthens the heart muscle, and lowers blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Regular physical activity can also contribute to weight management, as it helps burn calories and build lean muscle mass. Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for individuals with diabetes, as excess weight can worsen insulin resistance and increase the risk of complications.
Emotional and Mental Health Benefits:
Exercise not only benefits physical health but also has significant positive effects on emotional and mental well-being. Regular physical activity releases endorphins, which are natural mood-boosting chemicals in the brain. This can help reduce symptoms of stress, anxiety, and depression commonly experienced by individuals with diabetes. Staying active can also enhance self-confidence and improve overall well-being.
Types of Exercises for Diabetic Individuals:
Aerobic Exercises:
Aerobic exercises, also known as cardiovascular exercises, are beneficial for individuals with diabetes. These exercises increase heart rate and breathing rate, improving cardiovascular fitness. Some examples of aerobic activities suitable for different fitness levels include walking, cycling, swimming, dancing, and jogging. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, spread out over several days.
Strength Training:
Strength training exercises are essential for diabetic individuals as they help build and maintain muscle mass. Increased muscle mass improves insulin sensitivity, making it easier for cells to take up glucose from the bloodstream. It is recommended to engage in strength training activities at least twice a week. Exercises can include weightlifting, resistance band exercises, or bodyweight exercises such as push-ups and squats. Start with lighter weights or resistance and gradually increase as you build strength.
Flexibility and Balance Exercises:
Flexibility and balance exercises may not directly impact blood sugar levels, but they contribute to overall health and well-being. These exercises help improve joint flexibility, reduce the risk of falls, and enhance body awareness. Simple stretches, yoga, tai chi, and balance exercises can be done at home or in a class setting. Incorporate these exercises into your routine to improve mobility and reduce the risk of injury.
Tips for Incorporating Exercise into Daily Routine:
Setting Realistic Goals:
When starting an exercise routine, it's important to set realistic goals. Begin with small, achievable goals and gradually increase intensity and duration as you progress. Breaking down larger goals into smaller, manageable steps can help you stay motivated and avoid feeling overwhelmed. Celebrate each milestone achieved along the way to maintain enthusiasm and stay on track.
Finding Enjoyable Activities:
Exercise doesn't have to be boring. It's important to choose activities that you enjoy to make working out a fun and sustainable part of your routine. Consider activities such as dancing, hiking, swimming, or playing a sport. Finding a workout buddy or joining a group class can also make exercise more enjoyable and provide a sense of community.
Overcoming Barriers:
Identifying and addressing barriers to exercise is essential for maintaining a consistent routine. Lack of time, motivation, or access to facilities are common barriers that individuals face. To overcome these challenges, try incorporating physical activity into everyday tasks, such as taking the stairs instead of the elevator or walking or cycling to nearby destinations. Seek support from healthcare professionals, diabetes educators, or a support group to stay motivated and receive guidance tailored to your specific needs.
Conclusion:
Exercise plays a vital role in managing diabetes and reducing the risk of complications. It helps control blood sugar levels, improves heart health, promotes a healthy weight, and enhances emotional well-being. By incorporating various types of exercises into your routine and setting realistic goals, you can effectively manage your diabetes and lead a healthier, happier life. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise regimen to ensure it is safe and suitable for your individual needs. Stay active and prioritize exercise as part of your diabetes management plan. You've got this!
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
What are the benefits of exercise for managing diabetic complications?
Regular exercise can provide numerous benefits for managing diabetic complications. Here are some of the key advantages:
-
Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Exercise helps to increase insulin sensitivity, allowing your body to use insulin more efficiently. This can lead to better blood sugar control and reduced risk of complications.
-
Weight Management: Regular physical activity can help with weight loss or weight maintenance, which is important for diabetes management. Maintaining a healthy weight can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications.
-
Lower Blood Sugar Levels: Exercise helps to lower blood sugar levels by increasing glucose uptake by the muscles. This can help to reduce the need for medication and improve overall blood sugar control.
-
Cardiovascular Health: Regular exercise can improve cardiovascular health, reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke, which are common complications of diabetes. It helps to lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and strengthen the heart and blood vessels.
-
Stress Reduction: Exercise is a great stress reliever. It can help to reduce stress levels, promote relaxation, and improve overall mental well-being. Managing stress is important for people with diabetes, as stress can affect blood sugar levels.
-
Increased Energy Levels: Regular physical activity can boost your energy levels and improve overall stamina. This can make it easier to perform daily tasks and activities, enhancing your quality of life.
-
Better Sleep Quality: Exercise has been shown to improve sleep quality. Getting enough restful sleep is crucial for diabetes management as it can affect blood sugar control.
It is important to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any exercise program, especially if you have any existing medical conditions or complications. They can provide guidance and recommendations based on your individual needs and abilities. Remember to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts to avoid any potential risks or injuries. Regular exercise, when done safely and consistently, can be a valuable tool in managing diabetic complications and improving overall health.
How often should I exercise if I have diabetic complications?
If you have diabetic complications, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider before starting or changing any exercise routine. They will be able to provide personalized guidance based on your specific condition and needs. Generally, regular exercise is beneficial for managing diabetes and its complications. It can help improve blood sugar control, increase insulin sensitivity, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems.In terms of frequency, aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise spread throughout the week. This can be achieved by engaging in activities such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or dancing. Additionally, strength training exercises two to three times a week can help improve muscle strength and overall fitness.
However, it is crucial to listen to your body and not overexert yourself. Start slowly and gradually increase the duration and intensity of your workouts as tolerated. Be mindful of any symptoms or signs of low blood sugar or other complications during and after exercise. If you experience any concerning symptoms, it is important to stop exercising and seek medical attention.
Remember, consistency is key when it comes to exercise and diabetes management. By working closely with your healthcare provider and following their recommendations, you can develop an exercise routine that suits your individual needs and helps you maintain optimal health.
Can I exercise if I have other health conditions besides diabetes?
Yes, you can exercise if you have other health conditions besides diabetes. However, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any exercise regimen, especially if you have other health conditions. They will be able to provide personalized guidance and recommendations based on your specific situation.Regular exercise can have numerous benefits for overall health and well-being, including managing weight, improving cardiovascular health, boosting mood, and increasing energy levels. However, certain health conditions may require modifications to your exercise routine or specific precautions to be taken.
Your healthcare provider will take into consideration your other health conditions, medications you may be taking, and any potential risks or limitations that may affect your ability to exercise safely. They may also provide guidance on the type and intensity of exercise that is suitable for you.
Remember to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts. Listen to your body, and if you experience any discomfort or pain during exercise, stop immediately and consult with your healthcare provider.
In summary, while having other health conditions may require extra precautions, exercise can still be beneficial. Consult with your healthcare provider to create a safe and effective exercise plan that suits your individual needs and health conditions.
What types of exercises are best for managing diabetic complications?
When it comes to managing diabetic complications, incorporating a variety of exercises into your routine can be beneficial. Here are some types of exercises that are considered to be beneficial for individuals with diabetes:
-
Aerobic exercises: Engaging in activities that increase your heart rate and breathing such as walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling can help improve cardiovascular fitness and control blood sugar levels.
-
Strength training: Including resistance exercises like weightlifting or using resistance bands can help build muscle strength and improve insulin sensitivity.
-
Flexibility exercises: Stretching exercises like yoga or Pilates can improve flexibility, increase circulation, and reduce the risk of injury.
-
Balance exercises: Incorporating exercises that promote balance, such as tai chi or balance training, can help reduce the risk of falls and improve overall stability.
-
High-intensity interval training (HIIT): This form of exercise involves alternating between short bursts of intense activity and periods of rest. HIIT workouts have been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and cardiovascular fitness.
Remember to consult with your healthcare team before starting any exercise program to ensure it is safe and suitable for your specific needs. They can provide personalized guidance and help you develop an exercise plan that aligns with your fitness level and diabetic complications.